前言
前文说了在UE4中使用Python的方法,这篇文章就说一下在使用Python做UE4开发时常用的一些功能。
以下代码基于UE4.26,引擎自带的Python版本为3.7。
添加自定义菜单
这个功能可以在UE4的菜单栏上添加自定义的菜单,执行自定义的功能,方便用户使用。
import unreal menus = unreal.ToolMenus.get() main_menu = menus.find_menu("LevelEditor.MainMenu") # 获取unreal的菜单控件 added_menu = main_menu.add_sub_menu(main_menu.get_name(), "MyMenu", "我的菜单", "我的菜单") # 添加子菜单 entry = unreal.ToolMenuEntry( name='func1', type=unreal.MultiBlockType.MENU_ENTRY, insert_position=unreal.ToolMenuInsert('', unreal.ToolMenuInsertType.DEFAULT) ) # 按钮 entry.set_label('测试') entry.set_string_command(unreal.ToolMenuStringCommandType.PYTHON, "Name", 'print("测试一下")') # 设置按钮的功能 added_menu.add_menu_entry('MyMenu', entry) # 将按钮添加到子菜单 menus.refresh_all_widgets() # 刷新菜单ui
运行后生成的菜单如下
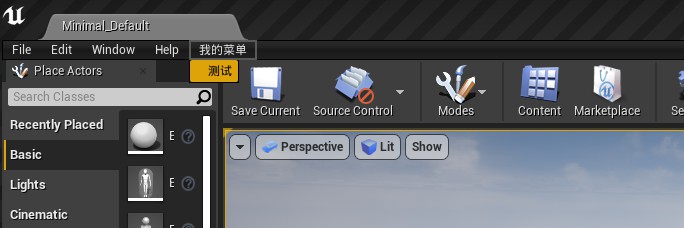
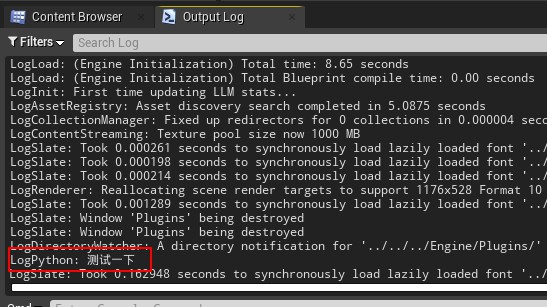
点击测试菜单命令后出现log如下
图形界面
在UE4中使用Python的PyQt库也可以制作图形界面,但因为UE4的图形界面是使用C++开发的,因此PyQt开发的页面是无法嵌入到UE4页面中的,这一点需要注意。
下面就来实现一个Qt窗口。
首先UE4自带的Python中没有PySide库,因此需要先给引擎自带的python(路径在Engine\Binaries\ThirdParty\Python3\Win64)安装PySide库。
pip install PySide2
另外同样由于UE4的图形界面是C++开发的,因此需要将Qt的窗口类与UE4的窗口进行关联,否则会导致UE4闪退或者卡死。
一个简单窗口的代码如下
import unreal from functools import partial from PySide2 import QtWidgets def __QtAppTick__(delta_seconds): QtWidgets.QApplication.sendPostedEvents() def bind_widget_to_unreal(widget): winid = widget.winId() unreal.parent_external_window_to_slate(winid) unreal_app = QtWidgets.QApplication.instance() if not unreal_app: unreal_app = QtWidgets.QApplication([]) tick_handle = unreal.register_slate_post_tick_callback(__QtAppTick__) __QtAppQuit__ = partial(unreal.unregister_slate_post_tick_callback, tick_handle) unreal_app.aboutToQuit.connect(__QtAppQuit__) w = QtWidgets.QWidget() bind_widget_to_unreal(w) w.show()
执行后效果如下
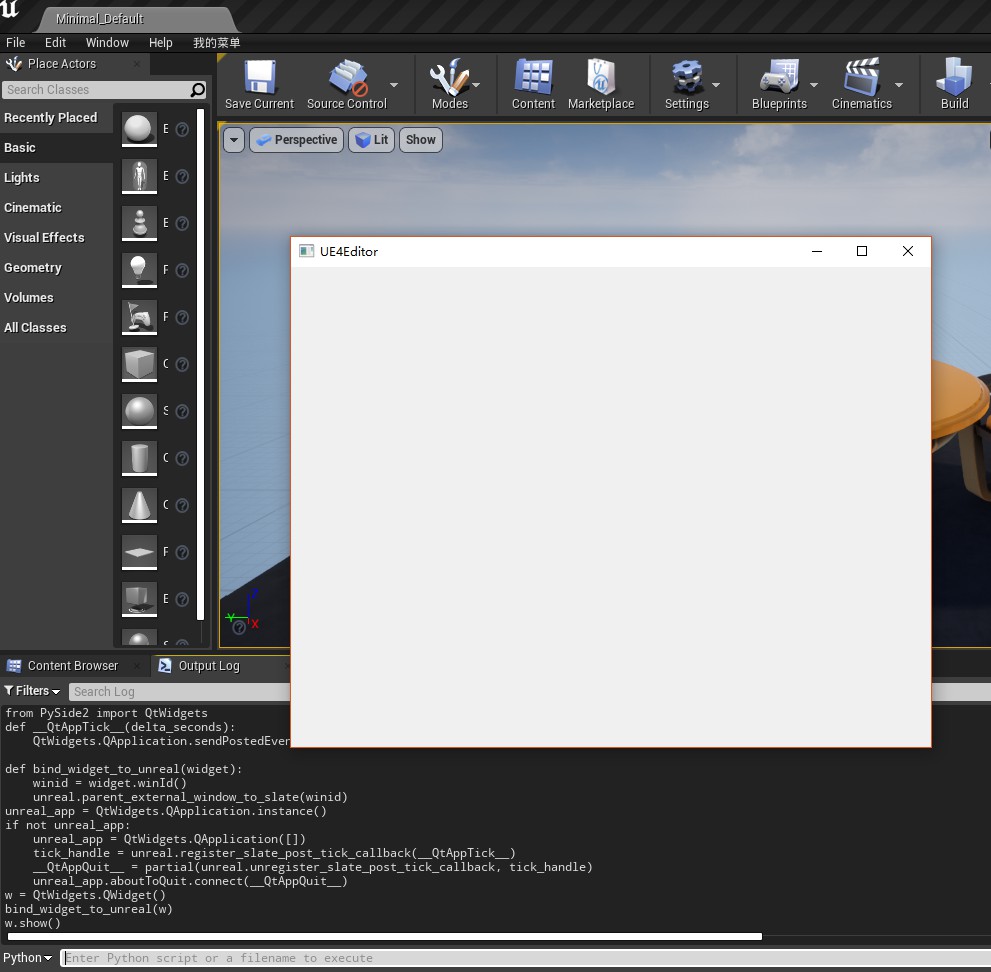
再结合QtDesigner制作的ui文件和通过Qt.py加载ui文件,就可以实现一个足够强大并且可以方便随时修改的UI窗口。
导入资产
对于图片、视频等资产的导入,实现是很简单的。
task = unreal.AssetImportTask() # 创建导入的任务 task.set_editor_property('automated', True) task.set_editor_property('destination_path', "/Game/test") task.set_editor_property('destination_name', "mypic") task.set_editor_property('filename', "D:/test.png") task.set_editor_property('replace_existing', True) # 替换已存在 task.set_editor_property('save', True) # 导入后保存 unreal.AssetToolsHelpers.get_asset_tools().import_asset_tasks([task]) # 执行导入任务
运行后,图片就被导入成功了。
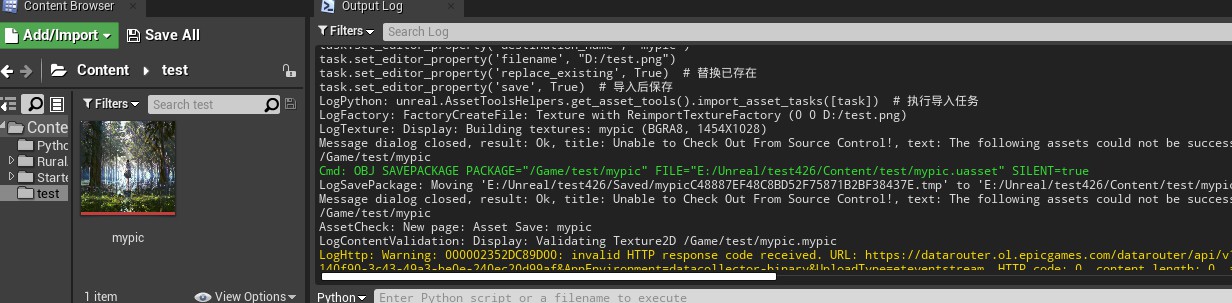
而对于fbx、abc、obj等模型文件的导入,就会比较复杂,在导入模型资产时会有如下这样的设置窗口。
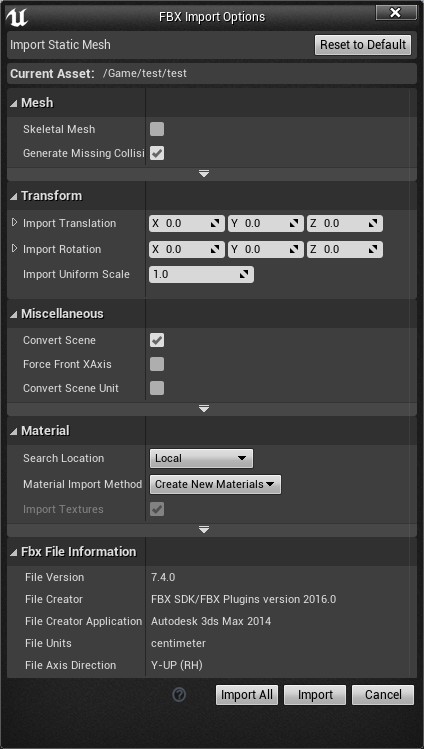
因此在使用Python导入模型资产时,也需要对这部分设置进行配置。
options = unreal.FbxImportUI() #声明导入配置 options.set_editor_property('import_mesh', True) options.set_editor_property('import_textures', False) #不导入材质 options.set_editor_property('import_materials', False) #不导入贴图 # 对于静态的fbx设置静态数据,包括合并网格,转换单位和方向等 options.set_editor_property('import_as_skeletal', False) options.static_mesh_import_data.set_editor_property('combine_meshes', True) options.static_mesh_import_data.set_editor_property('auto_generate_collision', False) options.static_mesh_import_data.set_editor_property('generate_lightmap_u_vs', False) options.static_mesh_import_data.set_editor_property('convert_scene', True) options.static_mesh_import_data.set_editor_property('convert_scene_unit', True) options.static_mesh_import_data.set_editor_property('vertex_color_import_option', unreal.VertexColorImportOption.REPLACE) task = unreal.AssetImportTask() # 创建导入的任务 task.set_editor_property('automated', True) task.set_editor_property('destination_path', "/Game/test") task.set_editor_property('destination_name', "fbx") task.set_editor_property('filename', "D:/test.fbx") task.set_editor_property('replace_existing', True) # 替换已存在 task.set_editor_property('save', True) # 导入后保存 # 将设置放到导入任务中 task.set_editor_property('options', options) unreal.AssetToolsHelpers.get_asset_tools().import_asset_tasks([task]) # 执行导入任务
导入后效果如下
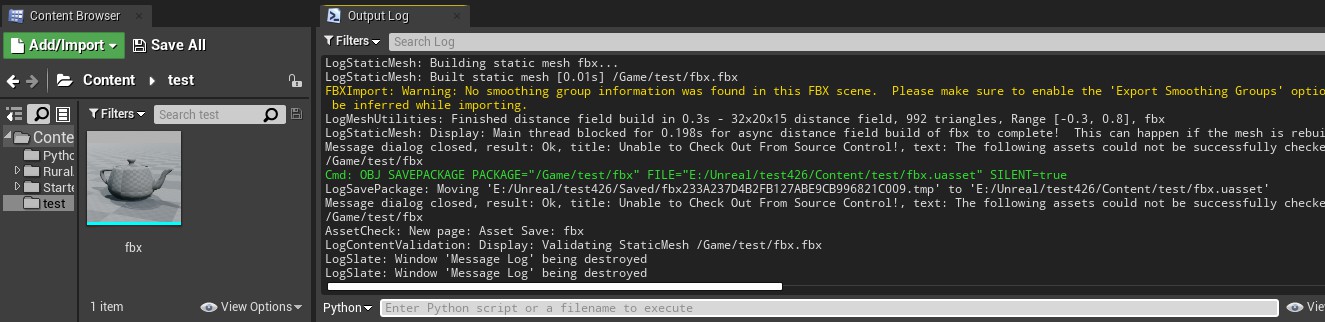
而在导入特效或毛发等文件时,会用到abc格式,这时候需要设置abc的导入配置。
另外由于轴向的问题,默认导入的物体朝向是错误的,需要修复。
# 修复abc的轴向问题 abc_conversion_settings = unreal.AbcConversionSettings( preset=unreal.AbcConversionPreset.MAYA, flip_u=False, flip_v=True, scale=[1.0, -1.0, 1.0], rotation=[90.0, 0.0, 0.0]) options = unreal.AbcImportSettings() #abc导入配置 options.set_editor_property('import_type', unreal.AlembicImportType.STATIC_MESH) options.set_editor_property('conversion_settings', abc_conversion_settings) task = unreal.AssetImportTask() # 创建导入的任务 task.set_editor_property('automated', True) task.set_editor_property('destination_path', "/Game/test") task.set_editor_property('destination_name', "abc") task.set_editor_property('filename', "D:/test.abc") task.set_editor_property('replace_existing', True) # 替换已存在 task.set_editor_property('save', True) # 导入后保存 # 将设置放到导入任务中 task.set_editor_property('options', options) unreal.AssetToolsHelpers.get_asset_tools().import_asset_tasks([task]) # 执行导入任务
效果如下
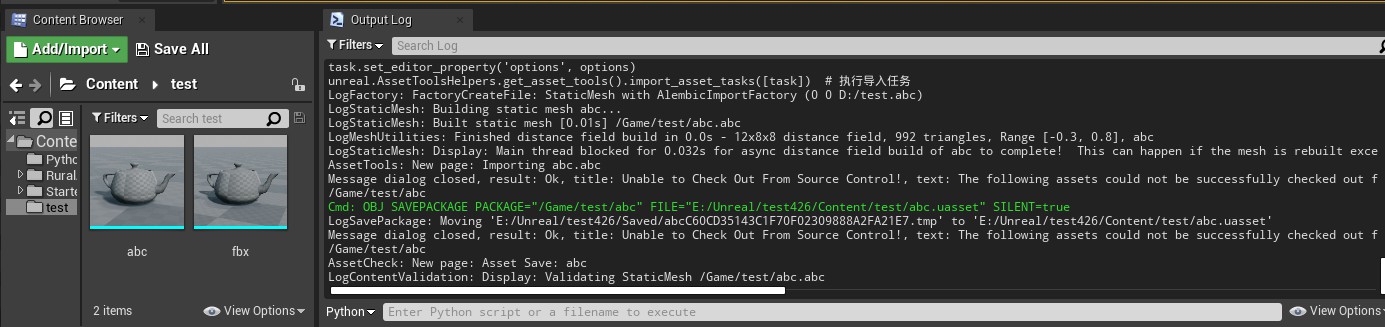
除了轴向以外,从Maya中导入模型时还需要注意世界比例导致的缩放问题。
其他功能
资产管理
# 创建文件夹 unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.make_directory('/Game/Test/NewDirectory') # 复制文件夹 unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.duplicate_directory('/Game/Test/OldDirectory', '/Game/Test/NewDirectory') # 删除文件夹 unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.delete_directory('/Game/Directory') # 重命名文件夹 unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.rename_directory('/Game/Directory', '/Game/NewDirectory') # 复制资产 unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.duplicate_asset('/Game/Test/Old', '/Game/Test/New') # 删除资产 unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.delete_asset('/Game/Test/File') # 判断资产是否存在 unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.does_asset_exist('/Game/Test/New') # 重命名资产 unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.rename_asset('/Game/Test/Old', '/Game/Test/New') #选择指定资产 paths = ['/Game/Test/abc','/Game/Textures/Sky/Cloud'] unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.sync_browser_to_objects(paths)
物体操作
# 从资产创建物体 asset = unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.load_asset("/Game/Test/Fbx") actor_location = unreal.Vector(0.0, 0.0, 0.0) actor_rotation = unreal.Rotator(0.0, 0.0, 0.0) unreal.EditorLevelLibrary.spawn_actor_from_object(asset, actor_location,actor_rotation) # 从蓝图实例化物体 actor_class = unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.load_blueprint_class('/Game/BluePrint/MyActor') actor_location = unreal.Vector(0.0, 0.0, 0.0) actor_rotation = unreal.Rotator(0.0, 0.0, 0.0) unreal.EditorLevelLibrary.spawn_actor_from_class(actor_class, actor_location, actor_rotation) # 获取场景中的所有物体 actors = unreal.EditorLevelLibrary.get_all_level_actors() # 获取场景中的所有组件 components = unreal.EditorLevelLibrary.get_all_level_actors_components() # 获取场景中所选的物体 unreal.EditorLevelLibrary.get_selected_level_actors() #在场景中选择物体 unreal.EditorLevelLibrary.set_selected_level_actors(actors_to_select) # 获取GameWorld world = unreal.EditorLevelLibrary.get_editor_world() # 获取场景中某类的物体 unreal.GameplayStatics.get_all_actors_of_class(unreal.EditorLevelLibrary.get_editor_world(), bpname) # 获取场景中有某tag的物体 unreal.GameplayStatics.get_all_actors_of_class(unreal.EditorLevelLibrary.get_editor_world(), tagname)
本文参考自影视后期流程小白的Unreal Python系列文章和Vanny Yuan的UnrealPython基础学习,有修改。
人生不能后悔,只能遗憾,
因为遗憾只是在感叹错过,
后悔却是否定了自己曾经的选择。
《一切都是最好的安排》
——辉姑娘






评论
还没有任何评论,你来说两句吧!